MODERN HYDROGRAPHIC AND WATER MANAGEMENT ZONING OF UKRAINE’S TERRITORY – IMPLEMENTATION OF THE WFD-2000/60/EC
Khilchevskyi V.K.1, Grebin V.V.1, Sherstyuk N.P.2
1Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine
2Oles Gonchar Dnipro National University, Dnipro, Ukraine
Corresponding author: Valentyn Khilchevskyi, Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, hilchevskiy@ukr.net
ABSTRACT
In contrast to the hydrological and hydrochemical zoning, hydrographic and water management zoning of Ukraine (2016) was created on a basin basis, taking into account the boundaries of river basins, and not physiographic zoning. The main function of hydrographic and water management zoning is water management. Primary is hydrographic zoning, and water management - based on it. The description of modern hydrographic zoning of the territory of Ukraine, approved in 2016 by the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine and included in the Water Code of Ukraine is given. Hydrographic zoning is carried out for the development and implementation of river basin management plans. On the territory of Ukraine nine areas of river basins are allocated: Dnipro; Dnister; Danube; Southern Bug; Don; Vistula; rivers of the Crimea; rivers of the Black Sea coast; rivers of the Azov Sea coast 13 sub-basins are allocated in four river basins district. The water management zoning is described - the division of hydrographic units into water management areas, which is carried out for the development of water management balances. In the regions of the river basins in the territory of Ukraine allocated 132 water management areas, 59 of which are located in the Dnipro basin. About 9,000 bodies of surface water allocated for monitoring in Ukraine. Approved zoning is the implementation of the provisions of the EU Water Framework Directive 2000/60 / EC in the management of water resources in Ukraine. Modern hydrographic and water management zoning of the territory of Ukraine approximates the management of water resources of the state to European requirements.
Keywords: hydrographic zoning, water management zoning, river basin district, sub-basin, water management area.
INTRODUCTION
The signing of the Association Agreement between Ukraine and the European Union (EU), which took place in 2014, opens up new opportunities and creates new standards in various spheres of public life, including the sphere of environmental protection. For Ukraine in the field of environmental protection, implementation of EU legislation takes place within the eight sectors regulated by 29 EU sources (EU directives and regulations) in this area. The directives and regulations establish common rules and standards that must be transposed (transposed) to domestic law. These rules and standards are not subject to discussion and should be fully achieved. EU law sources determine quantitative and qualitative indicators to be achieved by each country over a specified period of time.
In the Annex XXX of the Association Agreement between Ukraine and the EU, the following sectors related to environmental protection have been identified: 1) environmental management and integration of environmental policy into other sector policies; 2) the quality of atmospheric air; 3) management of waste and resources; 4) water quality and water management, including the marine environment; 5) nature protection; 6) industrial pollution and man-made threats; 7) climate change and protection of the ozone layer; 8) genetically modified organisms.
The European Union supports the implementation of the tasks facing each of the above sectors, funding from 2012 in Ukraine a technical assistance project called "Supplementing the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources of Ukraine with the implementation of sectoral budget support".
Questions related to the Water Quality and Water Management sector in the European Union are regulated by six major water directives: 1) Water Framework Directive, full name – Directive 2000/60 / EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 on the establishment of the framework for Community action in the field of water policy (Directive 2000/60/EC); 2) Flood Directive – Directive 2007/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2007 on the assessment and management of risks of flooding; 3) Marine Strategy Framework Directive – Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 on establishing a framework for Community action in the field of environmental policy relating to the marine environment; 4) Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive – Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 on urban waste water treatment; 5) Directive on drinking water– Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption; 6) Directive on nitrates – Council Directive 91/676 / EEC of 12 December 1991 on the protection of waters against pollution caused by nitrates from agricultural sources.
In Ukraine, water relations are regulated by the Water Code of Ukraine, adopted in 1995 (Water Code, 1995) and other acts.
PROBLEM STATEMENT AND SOURCE MATERIALS
Planned activities on implementation of EU Water Directives are being implemented in Ukraine. The schedule of achievement of goals for each of the directives, which specifies the terms of realization of certain tasks, has been developed. The most ambitious task is the implementation of the Water Framework Directive 2000/60/ EC, which are divided into stages in Ukraine.
The first stage (2014–2017) is the adoption of national legislation and determination of the authorized body; fixing at the legislative level the notion of unit of hydrographic zoning of the territory of the country; to develop a position on the basin management with the assignment of appropriate functions on it.
The second stage (2014–2020) is definition of areas of river basins and creation of mechanisms for management of international rivers, lakes and coastal waters; analysis of the characteristics of river basin districts; introduction of water quality monitoring programs.
The third stage (2014–2024) is preparation of river basin management plans, public consultation and publication of these plans.
The main task of this publication was to establish the dynamics of implementation of the WFD 2000/60/EC implementation plan in Ukraine, the characteristics of hydrographic zoning, approved by the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine in 2016, as well as the specifics of water management zoning.
For solving the problem, the open materials of the state bodies of Ukraine were used, as well as the author's own work, which took part in the development of the scheme of hydrographical zoning of the territory of Ukraine.
RESULTS OF RESERCH
From the three above-mentioned stages of the implementation of the WFD 2000/60/EU in Ukraine, the period of implementation of the first phase (2014-2017) – the legislative-organizational. Briefly describe its results.
On October 4, 2016, the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine adopted the Law of Ukraine "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of Ukraine on Implementation of Integrated Approaches in the Management of Water Resources Based on Basin Principle" (№ 1641-VIII), which introduced a number of changes to the Water Code of Ukraine in 1995, aimed at introducing the provisions of the Water Framework Directive of the European Union into the practice of water resources management of the state. This law supplemented the Water Code of Ukraine with a number of new terms and concepts implemented with WFD 2000/60/EC, officially approved the hydrographical zoning of the territory of the state, recognizing that the river basin district is the main unit of management in the field of water use and protection.
New terms included in the Water Code of Ukraine. Article 1 of the Water Code of Ukraine, entitled "Definition of the main terms", after the adoption of the Law of Ukraine № 1641-VIII of October 4, 2016, was supplemented by a number of new normative terms that are characteristic of the EU WFD. Here is a list of new terms: basin management principle, water sector, water management zoning, water management systems, hydrographic zoning, eutrophication, ecological cost, ecological state of a surface of an array of surface waters, substantially changed massif of surface waters, quantitative status of an array of groundwater, limestone, an array of surface waters, array of groundwater, redistribution of water resources, transitional water, river basin management plan, flood risk management plan, coastal waters, river basin district, river the basin (catchment), the sub-basin, the chemical status of the surface water body, the chemical status of the groundwater body (Khilchevskyi, Grebin, 2017).
The basic concept of "basin management principle" is integrated (integrated) water resources management within the area of the river basin, which is the main unit of management in the field of water use and protection and water reproduction. The area of the river basin consists of a river basin (adjacent river basins) and associated coastal and groundwater. The area of the river basin can be divided into smaller units – sub-basins. Sub-basin is part of a river basin, the flow of water from which due to the connected reservoirs and watercourses is carried out to the main river basin or water field downstream. The water management areas – part of the river basin, for which water balance is being developed, limits are set for the collection of water from the water object and other parameters of the use of the water object (water use).
It is envisaged to develop a river basin management plan – a document containing an analysis of the state and a set of measures for achieving the goals set for each river basin district within the established time frame. The river basin management plans and the procedure for their development are approved by the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine every six years.
It should be noted that the executive authorities in Ukraine in the field of water use and protection and reproduction of water resources have the following departments: the central executive body, which ensures the formation of state policy in the field of environmental protection – the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources of Ukraine, the central executive authority, which implements state policy in the field of water sector development (surface water) - the State Agency of Water Resources of Ukraine; central executive authority, which implements state policy in the field of geological study and rational use of subsoil (groundwater) – State Service of Geology and Subsoil of Ukraine; other bodies - in accordance with the law (Water Code, 1995).
Hydrological aspects of zoning of Ukrainian territory. For the territory of Ukraine (area 603,628 km2) four basic types of zoning are used: hydrological, hydrochemical, hydrographic and water management.
Hydrological zoning was developed in 1968 on the basis of information on the regime of small and medium rivers, is a classic type of zoning on a physic-geographic basis. It also entered the modern "National atlas of Ukraine" (Budkina, Kozintseva, 2007). This zoning reflects the spatial patterns of the hydrological regime of the rivers, the conditions for the formation of water balance, is closely related to the physical and geographical zoning (relief, climate, soil and vegetation cover). According to these indicators, the three highest taxa (hydrological countries) are allocated on the territory of Ukraine – the plains of Ukraine, the Ukrainian Carpathians and the Crimean Mountains. Further, the division takes place in hydrological regions and subregions.
In the flat part of Ukraine, three hydrological zones are distinguished: excessive water content
– covers the physical and geographical zone of mixed forests (the density of the river network is 0.250.5 km/km2, surface runoff is 3.0-4.5 L/s from 1 km2); sufficient water – corresponds to the forest-steppe physical and geographical zone (density of the river network is 0.4-0.8 km/km2, surface runoff - 1.74 L/s from 1 km2); lack of water – corresponds to the steppe zone (density of the river network in the south – 0.1-0.2 km/km2, surface runoff – 0.2-0.5 L/s from 1 km2, in the summer some rivers dry out).
In the Ukrainian Carpathians, the density of the river network is 1.0 km/km2 or more. The rivers are mountainous, with significant slopes and speeds. The water content of the rivers is highest in the upper reaches of the Tysa River and reaches 35 L/s from 1 km2, and in Transcarpathia – 15-25 L/s from 1 km2.
In the Crimean Mountains, the density of the river network reaches 0.6-0.7 km/km2, and surface runoff varies from 26 to 0.37 L/s from 1 km2. Hydrological regime is unstable, some rivers dry up.
Hydrochemical zoning reflects the spatial physic-geographical, climatic and geological conditions of the formation of the chemical composition of the water of small and medium rivers (Almazov, Konenko, Kuzmenko, 1978). But the connection with the physical and geographical zoning is not as clearly defined as in hydrological zoning, as the influence of local geological and soil conditions is given. In the hydrochemical zonation, the distribution areas of a particular hydrochemical type of water are allocated and the value of their total mineralization is indicated. The main hydrochemical types of water (according to predominant ions) are as follows: 1) hydrocarbonate-calcium; 2) hydrocarbonate-calcium-magnesium-sodium; 3) sulfate-hydrocarbonate-calcium-sodium; 4) sulfate-chloride-sodium-calcium; 5) chloride-sulfate-sodium.
In general, the total mineralization of water of small and medium rivers in Ukraine is increasing (from 200-300 mg/L to 1,500-3,000 mg/L or more) from northwest to southeast – from the Ukrainian Polesie to the Azov Sea coast. In the same direction there is a change of the abovementioned hydrochemical types of river waters (Khilchevskyi, Kurylo, Sherstyuk, 2018).
Hydrographic and water-management zoning of Ukraine are created on a basin basis, taking into account the boundaries of river basins, and not physical geographic zonation. For example, the largest area of the river basin of the Dnipro includes three physical-geographical zones: mixed forests, forest-steppe and steppe. In hydrographic zoning, the main taxonomic unit is the area of the river basin, which can be divided into sub-basins. The main function of hydrographic and water management zoning is water management, which can only be effective within the river basin. Primary is hydrographic zoning, and water management – based on it.
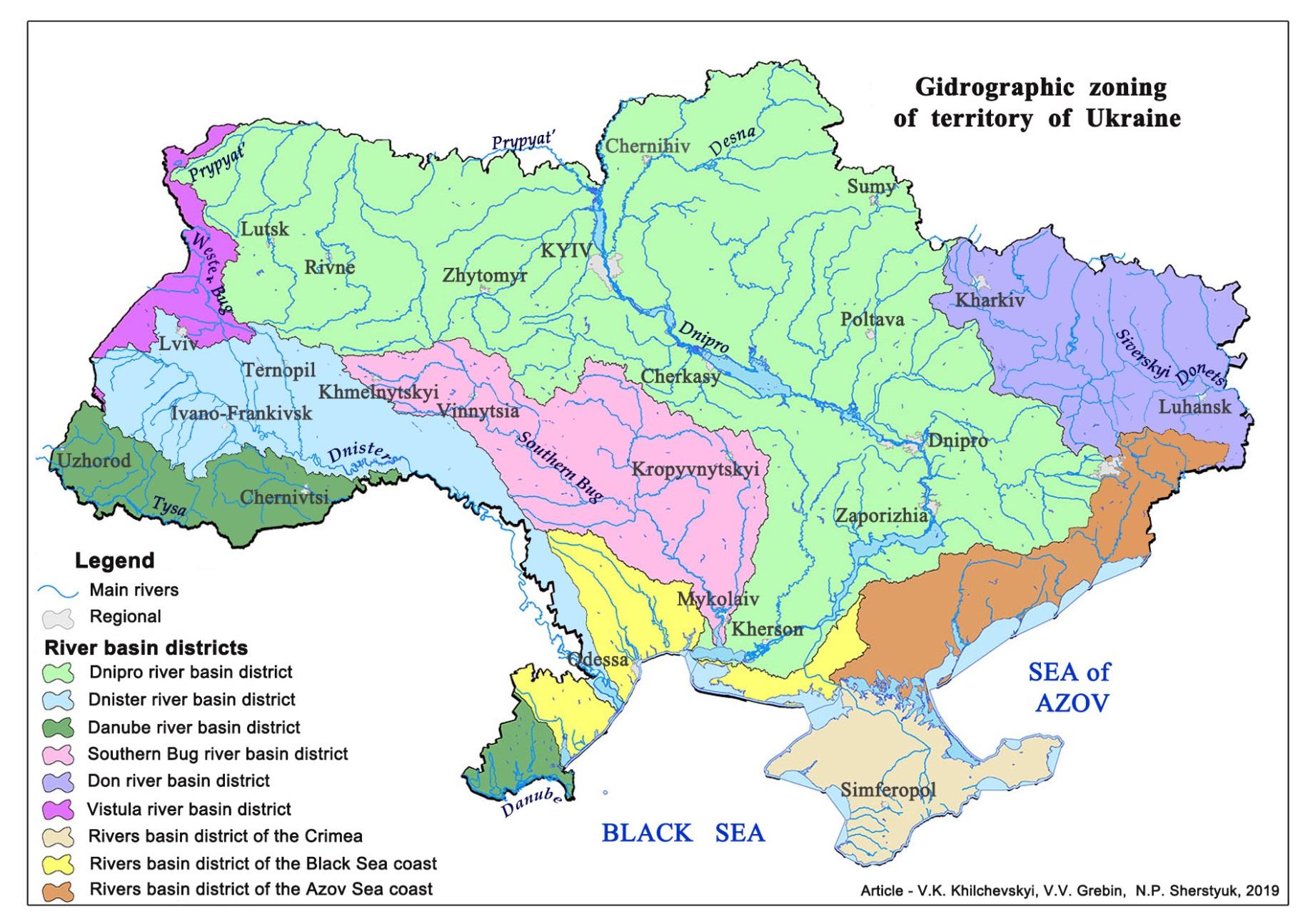
Hydrographic zoning of Ukrainian territory. Hydrographic zoning is the division of territory into a hydrographic unit, which is carried out to develop and implement river basin management plans. In 2013, a group of authors developed “Methods of hydrographic and water management zoning of the territory of Ukraine in accordance with the requirements of the Water Framework Directive of the European Union" (Methods, 2013). The work proposed the allocation of 9 river basin districts in Ukraine. In fact, this scheme of hydrographical zoning was approved by the Law of Ukraine No. 1641-VIII of October 4, 2016 In Ukraine, 9 river basin districts are legally approved: Dnipro river basin district; Dnister river basin district; Danube river basin district; Southern Bug river basin district; Don river basin district; Vistula river basin district; river basin district of the Crimea; river basin district of the Black Sea coast; river basin district of the Azov Sea coast (Fig. 1).
The law provides that within the established areas of river basins, the central executive body, which ensures the formation of state policy in the field of environmental protection, may allocate subbasins. The Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine in 2017 allocated 13 sub-basins within the four river basin districts: the Dnipro – 5 sub-basins, the Danube – 4 sub-basins, the Don – 2 sub-basins, the Vistula – 2 sub-basins (Names, 2017).
In the area of the Dnipro River basin, the following sub-basins are identified: the Upper Dnipro; the Middle Dnipro; the Lower Dnipro; the Prypyat River; the Desna River. In the area of the Danube River basin, the following sub-basins are identified: the Tysa River; the Prut River; the Siret River; Lower Danube. In the area of the Don River basin, the following sub-basins are singled out: the Siverskyi Donets River; Lower Don. In the area of the basin of the Vistula River, the following sub-basins are identified: the Western Bug River; the San River (Table 1). The Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources of Ukraine approves the boundaries of areas of river basins and sub-basins.
Fig. 1. Map diagram of the hydrographical zoning of the territory of Ukraine in 2016 by the river basin district
For detailing the hydrographic zoning of the territory of Ukraine, the development of a state water monitoring program, and the implementation of river basin management plans are allocated bodies water (for surface and groundwater). Bodies of surface water, are surface water bodies or their parts, for which environmental objectives are established and which are used to assess the achievement of these environmental objectives. In 9 districts of river basins on the territory of Ukraine, about 9,015 bodies of surface water have been allocated. In areas of river basins: Dnipro – 3,813 bodies of surface water (42 %); Dnister – 1,154 (13 %); Danube – 871 (10 %); Southern Bug – 1,089 (12 %); Don – 699 (8 %); Vistula – 249 (3 %); river basin district of the Crimea – 352 (4 %); river basin district of the Black Sea coast – 231 (2 %); river basin district of the Azov Sea coast – 557 (6 %).
Table 1. List of areas of river basins and sub-basins and the number of water management areas according to the hydrographical zoning of the territory of Ukraine in 2016
№ by order | The name of the river basin district | Catchment area, км2 | № by order | Sub-basin name | Catchment area, км2 | Number of water management areas |
1 | Dnipro river basin district | 296,315 | 1 | Upper Dnipro | 2,315 | 1 |
2 | Middle Dnipro | 109,527 | 23 | |||
3 | Lower Dnipro | 82,625 | 15 | |||
4 | Prypyat River | 68,366 | 13 | |||
5 | Desna River | 33,482 | 7 | |||
2 | Dnister river basin district | 53,961 | - | - | - | 12 |
3 | Danube river basin district | 30,625 | 1 | Tysa River | 12,810 | 3 |
2 | Prut River | 9,327 | 1 | |||
3 | Siret River | 2,070 | 1 | |||
4 | Lower Danube | 6,418 | 3 | |||
4 | Southern Bug river basin district | 63,700 | - | - | - | 11 |
5 | Don river basin district | 55,273 | 1 | Siverskyi Donets River | 54,901 | 19 |
2 | Lower Don River | 372 | 1 | |||
6 | Vistula river basin district | 12,892 | 1 | Western Bug River | 10,410 | 2 |
2 | San River | 2482 | 1 | |||
7 | River basin districts of the Crimea | 27,218 | - | - | - | 8 |
8 | River basin district of the Black Sea coast | 27,179 | - | - | - | 4 |
9 | River basin district of the Azov Sea coast | 36,866 | - | - | - | 7 |
Total | 9 | 604,742* | Total | 13 | 132 |
Note: 604,742* км2 - total area of 9 river basin district (including coastal waters);
603,628 км2 - the territory of Ukraine .
It should be noted that when optimizing the hydrographic zoning of the territory of Ukraine, the boundaries of ecoregions were specified, taking into account the passage of watershed lines and the elevation of water bodies above sea level as indirect factors, which have a preferential value in the absence of data on the composition of the hydrobiota (Grebin’ et al. 2016).
The conducted hydrographic zoning facilitates the study of hydrography and hydrochemistry of transboundary river basins located on the territory of Ukraine and other states (Khilchevskyi, Zabokrytska, Sherstyuk, 2018; Khilchevskiy, Grebin, Zabokrytska, 2019).
Water-management zoning of the territory of Ukraine. Water management zoning – the division of hydrographic units into water management areas, which is carried out for the development of water management balances. The number and boundaries of water areas are approved by the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine. The water management areas are distributed by river basin areas, taking into account the basin principle of management. In 2017, 132 water management areas were allocated (Names, 2017) – Table 2.
Table 2. List of water management areas within the rivers basins districts and sub-basins according to the hydrographical zoning of the territory of Ukraine 2016 (Names, 2017)
Code | Names of the rivers basins districts, | Catchment area, км2 |
1 | 2 | 3 |
М5.1 | 1. DNIPRO RIVER BASIN DISTRICT | 296,315 |
М5.1.1 | Sub-basin Upper Dnipro – water management areas: | 2,315 |
М5.1.1.01 | The Dnipro River from the state border to the beginning of the Kyiv reservoir (including the Sozh River within Ukraine) | 2,315 |
М5.1.2 | Sub-basin Middle Dnipro – water management areas: | 109,527 |
М5.1.2.02 | The Kyiv reservoir (including the Braginka River within Ukraine, excluding the Pripyat, Teteriv, Irpin rivers) |
2,324 |
М5.1.2.03 | The Dnipro River from the dam of the Kyiv reservoir to the dam of the Kaniv reservoir (excluding the Desna, Trubizh rivers) |
5,391 |
М5.1.2.04 | The Dnipro River from the dam of the Kaniv reservoir to the dam of the Kremenchug reservoir (excluding the Ros, Supiy, Sula, Tiasmyn rivers) | 8,751 |
М5.1.2.05 | The Teteriv River from the source to the gauging station Zhytomyr | 5,244 |
М5.1.2.06 | The Teteriv River from the gauging station Zhytomyr to the mouth of the Irsha River (including the Irsha River) |
6,230 |
М5.1.2.07 | The Teterev River from the mouth of the Irsha River to the mouth | 3,371 |
М5.1.2.08 | The Irpin River | 3,252 |
М5.1.2.09 | The Trubizh River | 3,636 |
М5.1.2.10 | The Ros River from the source to the boundary of the Kyiv and the Cherkasy regions | 9,412
|
М5.1.2.11 | The Ros River from the boundary of the Kyiv and the Cherkasy regions to the mouth | 3,263
|
М5.1.2.12 | The Supiy River | 2,065 |
М5.1.2.13 | The Sula River from the source to the border of the Sumy and Poltava regions | 4,544 |
М5.1.2.14 | The Sula River from the border of the Sumy and Poltava regions to the gauging station Lubny (excluding the Uday River) | 2,268
|
М5.1.2.15 | The Sula River from the gauging station Lubny to the mouth | 4,129 |
М5.1.2.16 | The Uday River | 6,835 |
М5.1.2.17 | The Tiasmyn River | 4,312 |
М5.1.2.18 | The Psel River from the state border to the border of the Sumy and Poltava regions | 3,899 |
М5.1.2.19 | The Psel River from the border of the Sumy and Poltava regions to the mouth of the Khorol River | 5,484 |
М5.1.2.20 | The Psel River from the mouth of the Khorol River to the mouth (excluding the Khorol River) | 3,929 |
М5.1.2.21 | The Khorol River | 3,952 |
Continuation of Table 2
1 | 2 | 3 | ||
М5.1.2.22 | The Vorskla River from the state border to the border of the Sumy and Poltava regions | 3,687 | ||
М5.1.2.23 | The Vorskla River from the border of the Sumy and Poltava regions to the mouth | 8,355 | ||
М5.1.2.24 | The Dnipro River from the dam of the Kremenchug reservoir to the dam of the Kamianske reservoir | 5,184 | ||
М5.1.3 | Sub-basin Lower Dnipro – water management areas: | 82,625 | ||
М5.1.3.25 | The Dnipro River from the dam of the Kamianske reservoir to the dam of the Dniprovsky reservoir (excluding the Oril, Samara rivers) | 5,859 | ||
М5.1.3.26 | The Dnipro River from the dam of the Dniprovsky reservoir to the dam of the Kakhovka reservoir | 19,197 | ||
М5.1.3.34 | The Gaychur River | 2,295 | ||
М5.1.3.35 | The Inhulets River from the source to the border of the Kirovograd and Dnipropetrovsk regions | 4,680
| ||
М5.1.3.36 | The Inhulets River from the border of the Kirovograd and Dnipropetrovsk regions to the border of the Dnipropetrovsk and Kherson regions (excluding the Saksahan River) | 2,680 | ||
М5.1.3.37 | The Inhulets River from the border of the Dnipropetrovsk and Kherson regions to the mouth | 5,522 | ||
М5.1.3.38 | The Saksahan River | 2,074 | ||
М5.1.3.39 | The Dnipro Liman | 1,906 | ||
М5.1.4 | Sub-basin the Prypyat River – water management areas: | 68,366 | ||
М5.1.4.40 | The Prypyat River from the source to the state border | 11,425 | ||
М5.1.4.41 | The Prypyat River from the gauging station of Mozyr to the mouth (within Ukraine) | 2,244 | ||
М5.1.4.42 | The Styr River from the source to the border of the Rivne and Volyn regions | 6,317 | ||
М5.1.4.43 | The Styr River within the Volyn region | 4,003 | ||
М5.1.4.44 | The Styr River from the border of the Volyn and Rivne regions to the state border | 2,457 | ||
М5.1.4.45 | The Horyn River from the source to the boundary of the Khmelnitskyi and Rivne regions | 4,243 | ||
М5.1.4.46 | The Horyn River from the border of the Khmelnytskyi and Rivne regions to the state border (excluding the Sluch River) | 8,776 | ||
М5.1.4.47 | The Sluch River from the source to the mouth of the Khomora River (including the Khomora River) | 4,835 | ||
М5.1.4.48 | The Sluch River from the mouth of the Khomora River to the mouth of the Korchyk River (including the Korchyk River) | 5,428 | ||
М5.1.4.49 | The Sluch River from the mouth of the Korchyk River to the mouth | 3,893 | ||
М5.1.4.50 | The Stvyha River | 2,966 | ||
М5.1.4.51 | The Ubort River from the source to the state border | 4,028 | ||
М5.1.4.52 | The Uzh River | 7,744 | ||
М5.1.5 | Sub-basin the Desna River – water management areas: | 33,482 | ||
М5.1.5.53 | The Desna River from the state border to the mouth of the Seym River | 7,091 | ||
М5.1.5.54 | The Desna River from the mouth of the Seym River to the stream gauge of Chernihiv (excluding the Seym, Snov rivers) | 6,433 | ||
М5.1.5.55 | The Desna River from the gauging stationof Chernihiv to the mouth (excluding the Oster River) | 4,176 | ||
М5.1.5.56 | The Seym River from the state border to the gauging station Mutyn | 4,856 | ||
М5.1.5.57 | The Seym River from the gauging station of Mutyn to the mouth | 2,479 | ||
Continuation of Table 2
1 | 2 | 3 | |
М5.1.5.58 | The Snov River | 4,983 | |
М5.1.5.59 | The Oster River | 3,450 | |
М5.2 | 2. DNISTER RIVER BASIN DISTRICT – water management areas: | 53,961 | |
М5.2.0.01 | The Dnister River from the source to the mouth of the Stryi River | 5,680 | |
М5.2.0.02 | The Stryi River | 2,899 | |
М5.2.0.03 | The Dnister River from the mouth of the Stryi River to the mouth of the Hnyla Lypa River | 5,842 | |
М5.2.0.06 | The Seret River | 3,994 | |
М5.2.0.07 | The Dnister River from the mouth of the River Seret to the stream gauge Mohyliv-Podilskyi (excluding the Zbruch River) | 9,613 | |
М5.2.0.08 | The Zbruch River | 3,406 | |
М5.2.0.09 | The Dnister River from the stream gauge Mohyliv-Podilskyi to the state border | 3,667 | |
М5.2.0.10 | The Dnister River from the state border to the mouth of the River Reut (within Ukraine) | 6,456 | |
М5.2.0.11 | The Dnister River from the mouth of the Byk River to the mouth (within Ukraine) | 6,456 | |
М5.2.0.12 | The Dnister Liman | 831 | |
М5.3 | 3. DANUBE RIVER BASIN DISTRICT | 30,625 | |
М5.3.1 | Sub-basin the Tysa River – water management areas: | 12, 810 | |
М5.3.1.01 | The Tysa River from the source to the state border | 8,848 | |
М5.3.1.02 | The Latorycia River from the source to the state border | 2,332 | |
М5.3.1.03 | The Uzh River from the source to the state border | 1,629 | |
М5.3.2 | Sub-basin the Prut River – water management area: | 9,327 | |
М5.3.2.04 | The Prut River from the source to the state border | 9,327 | |
М5.3.3 | Sub-basin the Siret River – water management area: | 2,070 | |
М5.3.3.05 | The Siret River from the source to the state border | 2,070 | |
М5.3.4 | Sub-basin Lower Danube - water management areas: | 6,418 | |
М5.3.4.06 | The Danube River from the state border to the mouth (excluding the Kahul, Yalpuh rivers) | 4,981 | |
М5.3.4.07 | The Kahul River (including the Kahul Lake) | 350 | |
М5.3.4.08 | The Yalpuh River (including the Yalpuh, Kuhurluy lakes) | 1,085 | |
М5.4 | 4. SOUTHER BUG RIVER BASIN DISTRICT – water management areas: | 63,700 | |
М5.4.0.01 | The Southern Bug River from the source to the mouth of the Ikva River (including the Ikva River) | 3,605 | |
М5.4.0.02 | The Southern Bug River from the mouth of the Ikva River to the gauging station Selyshche | 5,505 | |
М5.4.0.03 | The Southern Bug River from gauging station Selyshche to the mouth of the Silnytsia River (including the Silnytsia River) | 4,921 | |
М5.4.0.04 | The Southern Bug River from the mouth of the Silnytsia River to the mouth of the Synyukha River | 13,249 | |
М5.4.0.05 | The Tikych River (including the Hnyly Tikych, Hirsky Tikych rivers) | 6,723 | |
М5.4.0.06 | The Synyukha River (including the Velyka Vys River) | 9,978 | |
М5.4.0.07 | The Southern Bug River from the mouth of the Synyukha River to the gauging station Oleksandrivka | 2,163 | |
М5.4.0.08 | The Southern Bug River from stream gauge Oleksandrivka to the mouth (excluding the Inhul River) | 7,821 | |
Continuation of Table 2
1 | 2 | 3 | |
М5.4.0.09 | The Inhul River from the source to the mouth of the Berezivka River (including the Berezivka River) | 5,751 | |
М5.4.0.10 | The Inhul River from the mouth of the Berezivka River to the mouth | 4,086 | |
М5.4.0.11 | The Bug Liman | 603 | |
М6.5 | 5. DON RIVER BASIN DISTRICT | 55,273 | |
М6.5.1 | Sub-basin the Siverskyi Donets River – water management areas: | 54,901 | |
М6.5.1.01 | The Siverskyi Donets River from the state border to the dam of the Pechenízke reservoir | 2,424 | |
М6.5.1.02 | The Siverskyi Donets River from the dam of the Pechenízke reservoir to gauging station of the Zmiiv (excluding the Udy River) | 4,379 | |
М6.5.1.03 | The Udy River | 3,212 | |
М6.5.1.04 | The Siverskyi Donets River from the gauging station Zmiiv to the mouth of the Bereka River | 3,246 | |
М6.5.1.05 | The Bereka River | 2,668 | |
М6.5.1.06 | The Siverskyi Donets River from the mouth of the Bereka River to the boundary of the Kharkiv and Donetsk regions (excluding the Oskil River) | 1,044 | |
М6.5.1.07 | The Oskil River from the state border to the gauging station of Kupiansk | 1,923 | |
М6.5.1.08 | The Oskil River from the gauging station Kupiansk to the mouth | 2,006 | |
М6.5.1.09 | The Siverskyi Donets River from the border of Kharkiv and Donetsk regions to the border of the Donetsk and Luhansk regions (excluding the Kazennyi Torets, Bakhmutka rivers) | 1.895 | |
М6.5.1.10 | The Kazennyi Torets River | 5,204 | |
М6.5.1.11 | The Bakhmutka River | 1,932 | |
М6.5.1.12 | The Siverskyi Donets River from the border of the Donetsk and Luhansk regions to the gauging station Lysychansk (excluding the Krasna, Borova) | 840 | |
М6.5.1.13 | The Krasna River | 3,332 | |
М6.5.1.14 | The Borova River | 1,914 | |
М6.5.1.15 | The Siverskyi Donets River from the gauging station Lysychansk to the state border (excluding the Aidar, Luhan, Derkul rivers) | 4,577 | |
М6.5.1.16 | The Aidar River | 5,085 | |
М6.5.1.17 | The Luhan River | 3,726 | |
М6.5.1.18 | The Derkul River | 3,795 | |
М6.5.1.19 | The Velyka Kamianka River (within Ukraine) | 1,619 | |
М6.5.2 | Sub-basin Lower Don River – water management areas: | 372 | |
М6.5.2.20 | Tributaries of the Don River (within Ukraine) | 372 | |
А6.6 | 6. VISTULA RIVER BASIN DISTRICT | 12,892 | |
А6.6.1 | Sub-basin Western Bug River – water management areas: | 10,410 | |
А6.6.1.01 | The Western Bug River from the source to the state border | 6,241 | |
А6.6.1.02 | The Western Bug River from the state border with the Republic of Poland to the state border with the Republic of Belarus | 4,168 | |
А6.6.2 | Sub-basin San River – water management area: | 2,482 | |
А6.6.2.03 | The San River and its tributaries (within Ukraine) | 2,361 | |
М5.7 | 7. RIVER BASIN DISTRICT OF THE CRIMEA – water management areas: | 27,218 | |
М5.7.0.01 | The western coast of the Crimean peninsula (excluding the Kacha, Alma, Chorna, Belbek rivers) | 8,327 | |
М5.7.0.02 | The Kacha River | 669 | |
М5.7.0.03 | The Alma River | 685 | |
Continuation of Table 2
1 | 2 | 3 |
М5.7.0.04 | The Chorna River | 628 |
М5.7.0.05 | The Belbek River | 499 |
М5.7.0.06 | The Southern coast of the Crimean peninsula | 3,410 |
М6.7.0.07 | The coast of the Azov Sea within the Crimean peninsula (excluding the Salhyr River) | 8,502 |
М5.8 | 8. RIVER BASIN DISTRICT OF THE BLACK SEA COAST – water management areas: | 27,179 |
М5.8.0.01 | The Black Sea coast between the mouth of the Danube River and the Dnister Liman |
6,211 |
М6.7.0.08 | The Salhyr River | 4,280 |
М5.8.0.02 | The Black Sea coast between the Dnister Liman and the Dnipro Lyman (excluding the Tylihul River with estuary) | 9,425 |
М5.8.0.03 | The Tylihul River with estuary | 5,506 |
М5.8.0.04 | The Black Sea coast between the Dnipro Lyman and the Crimean peninsula | 4,424 |
М.6.9 | 9. RIVER BASIN DISTRICT OF THE AZOV SEA COAST – water management areas: | 36,866 |
М6.9.0.01 | The coast of the Azov Sea from the Crimean peninsula to the state border (excluding the Molochna, Berda, Kalmius, Mius rivers) | 8,502 |
М6.9.0.02 | The Molochna River (including the Molochnyi Lyman) | 5,493 |
М6.9.0.03 | The Berda River | 1,904 |
М6.9.0.04 | The Kalmius River (excluding the Kalchik River) | 3,782 |
М6.9.0.05 | The Kalchik River | 1,302 |
М6.9.0.06 | The Mius River from the source to the state border (excluding the Krynka River) | 2,365 |
М6.9.0.07 | The Krynka River from the source to the state border | 2,572 |
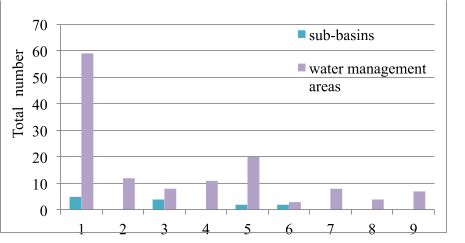
According to the river basin districts, the distribution 132 of water management areas is as follows: Dnipro – 59 (45 %); Dnister – 12 (9 %); Danube – 8 (6 %); Southern Bug – 11 (8 %); Don – 20 (16 %); Vistula – 3 (2 %); rivers of the Crimea – 8 (6 %); rivers of the Black Sea coast – 4 (3 %); rivers of the Azov Sea coast – 7 (5 %) - Fig. 2.
In order to ensure the compilation of the state water cadastre in the section "Water Utilization", the coding of areas of river basins, sub basins and water areas is carried out (see Table 2). The code of the area of the river basin is formed from three characters: the first two characters are the code of the sea: A6 – the Baltic Sea, M5 – the Black Sea, M6 – the Azov Sea; the third sign is the serial number of the river basin district. The code for the sub-basin is formed from four characters: the first three characters are the code of the river basin district; the fourth sign is the serial number of the subbasin within the corresponding of the river basin district. The code of the water management areas formed from six characters: the first three characters are the code of the river basin district, the fourth sign is the serial number of the sub-basin within the corresponding of the river basin district (in the absence of sub basins, the fourth sign is 0), the fifth and sixth signs are the serial number of the water management area within the respective of the river basin district.
As noted, water management areas are allocated for the development of water management balance for certain areas. The water management balances the ratio between available for use of water resources in a certain area and the needs of them within a certain region for a certain period of time. On the basis of water management balances, water intake limits from the water body and other parameters of the use of the water object (water use) are set by different water users representing industry, housing and communal services and agriculture. Water management balances an important mechanism for regulating access to water resources in Ukraine and its individual regions.
Fig. 2. Presence of sub-basins and water management areas within the rivers basins districts according to the hydrographical zoning of the territory of Ukraine in 2016:
1 – Dnipro; 2 – Dnister; 3 – Danube; 4 – Southern Bug; 5 – Don; 6 –Vistula;
7 – rivers of the Crimea; 8 – rivers of the Black Sea coast; 9 – rivers of the Azov Sea coast
The flow of rivers of Ukraine without the Danube averages 87.1 km3 per year, of which 52.4 km3 (60%) is formed on the territory of the country. A further 123 km3/year passes along the Kiliya branch of the Danube (the border between Ukraine and Romania). Thus, the total flow of all rivers in Ukraine is 210.1 km3/year. With the population in Ukraine in 2013, 45.5 million people water availability indicators for 1 person is: 1.15 thousand m3/year - local flow rivers; 1.91 thousand m3/year - the total river flow of Ukraine without the Danube; 4.62 thousand m3/year - the total flow of Ukrainian rivers along with the Danube. And if we take into account the downward trend in the population in Ukraine, in particular, in 2019 - 42.153 million people (Population, 2019), then we will get the following water availability indicators for 1 person: 1.24 thousand m3/year - local flow rivers; 2.07 thousand m3/year - the total river flow of Ukraine without the Danube; 4.98 thousand m3/year - the total flow of Ukrainian rivers along with the Danube.
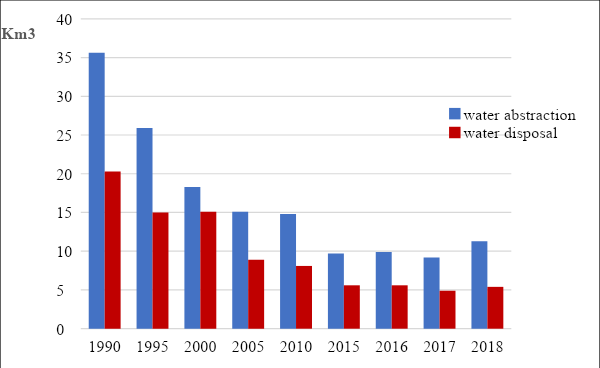
It should be noted that during 1991-2000, Ukraine experienced a sharp economic decline (2.5 times), after which a certain rise began. Analysis of water use statistics also shows that water withdrawal from natural reservoirs in Ukraine has been declining since 1990 (Table 3, Fig. 3.).
Table 3. Water abstraction from water bodies, its use and water disposal in Ukraine in 1990–2018 (including fresh and sea water), km3 (Main indicators, 2019)
Indicator / years | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2013 | 2014* | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
Water abstraction from water bodies | 35.6 | 25.9 | 18.3 | 15.1 | 14.8 | 13.6 | 11.5 | 9.7 | 9.9 | 9.2 | 11.3 |
Total water disposal | 20.3 | 15.0 | 11.0 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 7.7 | 6.6 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 4.9 | 5.4 |
Note. * - starting from 2014, information was submitted without including data on the temporarily occupied territory of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and part of the anti-terrorist operation zone in the Donbass.
The maximum water intake was reached in 1990, when 35.6 km3 of water abstraction from natural water bodies. In 2000, water abstraction decreased by 1.9 times (18.3 km3) compared to 1990. In 2010, water abstraction decreased by 2.4 times (14.9 km3), and in 2013 - by 2.6 times (13.6 km3). In 2014-2018 this figure was 9.2-11.5 km3. In the same proportions, total water disposal also decreased.
The structure of water use in Ukraine by major sectors of the economy varies by year (Table 4). In some years, it is very close to European proportions. The largest water in Ukraine is used by industry - 45-63%; agriculture - 16-34%; housing and communal services - 17-28% (during 1995-2015). In Europe, the water use structure is as follows: 54% - industry; 25% - agriculture; 21% - housing and communal services (Water uses FAO's, 2016).
Fig. 3. Water abstraction from water bodies and total water disposal in Ukraine
in 1990-2018, km3
Table 4. Structure of water use in Ukraine in various sectors of the economy 1995-2015, %
(National report, 2000, 2010, 2015)
Activity/years | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 |
Industry | 45 | 49 | 56 | 61 | 63 |
Agriculture | 34 | 24 | 16 | 19 | 20 |
Housing and communal services | 21 | 27 | 28 | 21 | 17 |
In order to further implement the plan of implementation of the provisions of the WFD 2000/60/EC, the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine approved the "Procedure for the development of a river basin management plan" (2017); «The procedure for conducting state water monitoring» (2018).The Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources of Ukraine approved the following documents: "The Procedure for the Development of Water Balances" (2017); "Typical position for the basin councils" (2017); "List of pollutants for the determination of the chemical status of surface and groundwater arrays and the ecological potential of an artificial or substantially modified surface water body" (2017); «Methodology for the determination of surface and ground water bodies» (2019).
CONCLUSIONS
- The first stage of the implementation of the Water Framework Directive 2000/60 / EC in Ukraine was completed successfully.
- Approved in 2016 at the legislative level, the hydrographic zoning of the territory of Ukraine meets the requirements of the Water Framework Directive of the European Union.
- The main unit of hydrographical zoning is the area of the river basin, which in Ukraine is allocated nine (Dnipro, Dnister, Danube, Southern Bug, Don, Vistula, rivers of the Crimea; rivers of the Black Sea coast; rivers of the Azov Sea coast).
- Within the four of the nine river basin districts, 13 sub-basins are allocated on the territory of Ukraine: a) Dnipro river basin district– the sub-basins of the Upper Dnipro, the Middle Dnipro, the Lower Dnipro, the Prypyat River, the Desna River; b) Danube river basin district- sub-basins the Tysa River, the Prut River, the Siret River, Lower Danube; c) Don river basin district – sub-basins the Siverskyi Donets River, Lower Don; d) Vistula river basin district– the sub-basins of the Western Bug River, the San River.
- Bodies of surface water are surface water bodies or their parts, for which environmental objectives are established and which are used to assess the achievement of these environmental objectives. About 9000 bodies of surface water were allocated in the areas of river basins in Ukraine.
- The main division of water zoning is water management area. In river basins of Ukraine, 132 water management area were allocated, of which 59 are located in the Dnieper basin. They are allocated for the calculation of water availability indicators for individual regions.
- Water use in Ukraine today (about 10 km3) has significantly decreased compared to the 1990 high (35.6 km3).
- Modern hydrographic and water management zoning of the territory of Ukraine approximates the management of water resources of the state to European requirements.
REFERENCES
- Almazov A.M., Konenko A.D., Kuzmenko N.M. Hydrochemical zoning: map S 1:12 000 000 / Atlas of natural conditions and natural resources of the Ukrainian SSR. Moscow. 1978. P. 112. In Russian. [Алмазов А.М., Коненко А.Д. Гидрохимическое районирование: карта М 1:12 000 000 / Атлас природных условий и естественных ресурсов Украинской ССР. Москва. 1978. С. 112].
- Budkina L.H., Kozintseva L.M. Hydrological zoning: map S 1:8 000 000 / National Atlas of Ukraine. Kyiv. 2007. P. 184. In Ukrainian. [Будкіна Л.Г., Козінцева Л.М. Гідрологічне районування: карта М 1: 8 000 000 / Національний атлас України. Київ.2007. С. 184].
- Grebin’ V.V., Mokin V.B., Kryzhanivskiy Е.M., Afanasyev S.A. Optimization of Hydrographic and Water-management Regionalization of Ukraine according to World Approaches and Principles of the EU Water Framework Directive. Hydrobiological Journal. 2016. Vol. 52(5). P. 81-92. DOI: 10.1615/HydrobJ.v52.i5.90.
- Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal EU. L 327. 22/12/2000. P. 0001-0073.
- Khilchevskiy V.K., Grebin V.V., Zabokrytska M.R. Abiotic Typology of the Rivers and Lakes of the Ukrainian Section of the Vistula River Basin and its Comparison with Results of Polish Investigations. Hydrobiological Journal. 2019. Vol. 55(3). P. 95-102. DOI: 10.1615/HydrobJ.v55.i3.110.
- Khilchevskyi V.K., Grebin V.V. Hydrographic and hydroeconomic zoning of the territory of Ukraine, approved in 2016 - implementation of the provisions of the EU WFD. Hydrology, hydrochemistry and hydroecology. 2017. № 1(44). P. 8-20. In Ukrainian. [Хільчевський В.К., Гребінь В.В. Гідрографічне та водогосподарське районування території України, затверджене у 2016 р. – реалізація положень ВРД ЄС. Гідрологія, гідрохімія і гідроекологія. 2017. № 1(44). С. 8-20].
- Khilchevskyi V.К., Kurylo S.М., Sherstyuk N.P. Chemical composition of different types of natural waters in Ukraine. Journal of Geology, Geography and Geoecology. 2018. Vol. 27(1). P. 68-80. https://doi.org/10.15421/111832.
- Khilchevskyi V.K., Zabokrytska M.R., Sherstyuk N.P. Hydrography and hydrochemistry of the transboundary river Western Bug on territory of Ukraine. Journal of Geology, Geography and Geoecology. 2018. Vol. 27(2). P. 232-243. https://doi.org/10.15421/111848.
- Main indicators of water use and protection. State Statistics Service of Ukraine. 2019. In Ukrainian. [Основні показники використання та охорони водних ресурсів. Державна служба статистики України. 2019]. http://www.ukrstat.gov.ua.
- Methods of hydrographic and water management zoning of the territory of Ukraine in accordance with the requirements of the European Union Water Framework Directive / V.V. Grebin, V.B. Mokin, V.A Stashuk, V.K. Khilchevskyi, M.V. Yatsiuk, O.V. Chunarov, Ye.M. Kryzhanivskyi, V.S. Babchuk, O.Ye. Yaroshevych. Kyiv. 2013. Interpres. 55 p. In Ukrainian. [Методики гідрографічного та водогосподаського районування території України відповідно до вимог Водної рамкової директиви Європейського Союзу / В.В. Гребінь, В.Б. Мокін, В.А. Сташук, В.К. Хільчевський, М.В. Яцюк, О.В. Чунарьов, Є.М. Крижанівський, В.С. Бабчук, О.Є. Ярошевич. Київ. Інтерпрес. 2013. 55 с.].
- Names of sub-basins and water management areas within river basin districts / Annex to the Order of the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine dated January 26, 2017 No. 25. In Ukrainian. In Ukrainian. [Назви суббасейнів та водогосподарських ділянок у межах районів річкових басейнів / Додаток до наказу Міністерства екології та природних ресурсів України від 26.01.2017. № 25]. http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/z0208-17.
- National report on the state of the environment in Ukraine in 2000. Kiev. Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine. 2001. 184 p. In Ukrainian. [Національна доповідь про стан навколишнього природного середовища в Україні у 2000 році. Київ. Міністерство екології та природних ресурсів України. 2001. 184 с.]
- National report on the state of the environment in Ukraine in 2010. Kiev. Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine. 2011. 254 p. In Ukrainian. [Національна доповідь про стан навколишнього природного середовища в Україні у 2010 році. Київ. Міністерство екології та природних ресурсів України. 2011. 254 с.]. https://menr.gov.ua/news/31174.html.
- National report on the state of the environment in Ukraine in 2015. Kiev. Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine. 2017. 308 p. In Ukrainian. [Національна доповідь про стан навколишнього природного середовища в Україні у 2015 році. Київ. Міністерство екології та природних ресурсів України. 2017. 308 с.]. https://menr.gov.ua/news/31768.html.
- Population (estimated) as of January 1, 2019, and average population in 2018. State Statistics Service of Ukraine. 2019. In Ukrainian. [Чисельність населення (за оцінкою) на 1 січня 2019 року. та середня чисельність у 2018 році. Державна служба статистики України. 2019]. http://www.ukrstat.gov.ua/operativ/operativ2018/ds/kn/kn_u/kn1218_u.html.
- Water Code of Ukraine, 1995 (with amendments from 2000-2016 year. In Ukrainian. [Водний кодекс України, 1995 р. (зі змінами і доповненнями 2000-2016 рр.)]. http://zakon.rada.gov.ua/go/213/95-вр.
- Water uses FAO's Information System on Water and Agriculture. Aquastat. 2016. http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/water_use/index.stm.